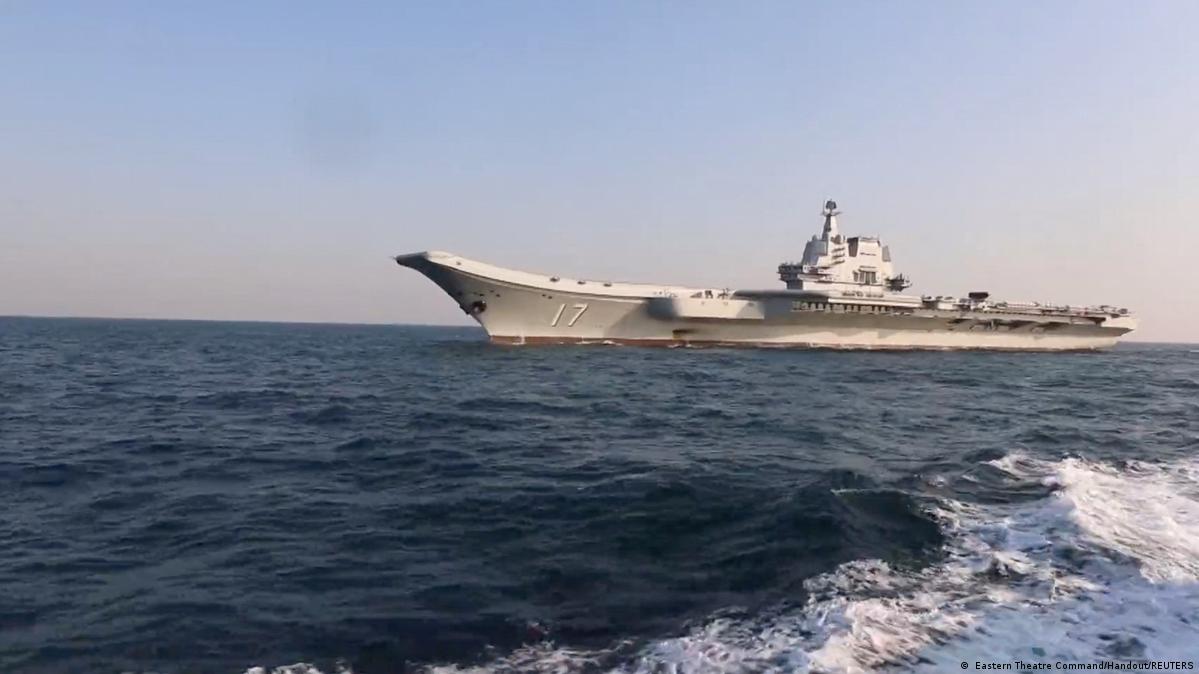
China Taiwan drills: Tensions between China and Taiwan have escalated once again as Beijing launches its latest series of large-scale military drills around the island. Codenamed “Justice Mission 2025,” these operations involve the Chinese army, navy, air force, and rocket force in what officials describe as a rehearsal for blockading and seizing key Taiwanese regions. Although China frequently conducts exercises near Taiwan, the timing, intensity, and messaging around these China Taiwan drills have drawn global attention.
The drills come shortly after the United States announced one of its biggest-ever arms packages to Taiwan—an $11 billion sale that includes advanced missile systems and surveillance technology. Beijing’s strong reaction, including sanctions against American defense companies, highlights how sensitive Washington’s military support for Taipei has become.
For Taiwan, China’s actions represent not just military intimidation but also an attempt to influence regional politics, international diplomacy, and the island’s domestic confidence. Taiwan’s government has condemned the exercises as a threat to global norms and regional stability, while its military remains on high alert.
As geopolitical anxieties rise, these China Taiwan drills have become a crucial test of strength, signalling how Beijing intends to shape the future of the Taiwan Strait in 2025 and beyond.
China Taiwan drills: Historical Context Why the Taiwan Strait Remains a Global Flashpoint
Understanding the impact of the current drills requires looking at the long, tense, and complicated history between China and Taiwan. Although the two sides share cultural and historical links, their political paths diverged after the Chinese Civil War ended in 1949. The defeated Nationalist government retreated to Taiwan, while the Communist Party established the People’s Republic of China in Beijing.
Since then, Beijing has viewed Taiwan as a breakaway province, while most Taiwanese citizens see themselves as living in a self-governed, democratic society. Over the decades, the Taiwan Strait has witnessed several crises, including military standoffs, missile tests, and diplomatic conflicts.
Key historical turning points: China Taiwan drills
- 1995–1996 Taiwan Strait Crisis: China fired missiles to influence Taiwan’s first direct presidential election.
- 2005 Anti-Secession Law: Beijing declared it would use “non-peaceful means” if Taiwan attempts formal independence.
- 2022 Pelosi Visit: China launched unprecedented live-fire drills, seen as a simulated blockade.
- 2024 Lai Ching-te’s Inauguration: Beijing intensified pressure, labeling Lai a “separatist.”
With every new military exercise, China reinforces its message: it will respond forcefully to any move it interprets as supporting Taiwan’s independence.
Why China Announced “Justice Mission 2025” Now
China’s decision to hold the latest China Taiwan drills is driven by multiple strategic, political, and military considerations. Although Beijing claims the exercises are routine, several developments have clearly provoked a sharper reaction.
1. The $11 Billion US Arms Sale to Taiwan
Just days before the drills were announced, Washington approved a major arms package that included:
- Long-range missile systems
- Advanced surveillance radars
- Air defense upgrades
- Support equipment for Taiwan’s growing asymmetric warfare strategy
Beijing condemned the deal as a serious violation of the “One China” principle, arguing that the US is fueling separatist forces.
2. Taiwan’s Intensified Military Modernisation
Since taking office, President Lai Ching-te has pushed for stronger defense capabilities. His government:
- Increased defense spending
- Expanded missile production
- Launched indigenous submarine development
- Announced a “dome-like” air defense network
Beijing views Lai as an advocate for independence and sees any military enhancement as a direct challenge.
3. Japan’s Recent Comments on Taiwan
Japan’s leader Sanae Takaichi recently suggested that Tokyo’s self-defense forces might intervene if China attacks Taiwan. This statement sparked outrage in Beijing and contributed to rising regional tensions.
4. A New Commander in Charge of Taiwan Operations
This marks the first major drill led by Yang Zhibin, the newly appointed head of the Eastern Theater Command. Military analysts believe new commanders often seek to demonstrate strength early in their tenure.
How China Plans Its Strategy: Understanding the Objectives of the China Taiwan drills
China’s military does not conduct large-scale operations without clear goals. The China Taiwan drills appear to be organised around several connected objectives that extend far beyond simple training.
1. Demonstrating China’s Ability to Encircle Taiwan
The Eastern Theater Command announced that the drills simulate:
- A full blockade of the island
- Targeted strikes on military bases
- Control over major sea and air routes
- Cutting off foreign military support
This is significant because a blockade is considered China’s most realistic strategy if it decides to apply major military pressure without launching a full invasion.
2. Testing Multi-Branch Combat Coordination
The drills involve:
- The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Army
- The PLA Navy (PLAN)
- The PLA Air Force (PLAAF)
- The PLA Rocket Force (PLARF)
By involving all branches, China is refining joint-force warfare—essential for any future operation around Taiwan.
3. Sending a Political Warning to Taiwan’s Government
China often uses military pressure as political messaging. By calling the drills a “shield of justice,” Beijing is framing its actions as defensive rather than offensive. The message is clear:
“Moves toward independence will be met with overwhelming force.”
4. Deterring External Military Support
China is deeply concerned about Taiwan receiving foreign military backing, especially from:
- The United States
- Japan
- Australia
By practicing blockades and long-range strikes, China aims to signal that outside intervention would be risky and costly.
5. Strengthening Domestic Support for the Communist Party
Military displays also serve internal purposes. China uses demonstrations of power to reinforce national pride, unity, and support for the government.
6. Testing Real-World Combat Readiness
Live-fire drills help the PLA evaluate:
- Missile accuracy
- Pilot performance
- Naval coordination
- Cyber and electronic warfare
- Response to simulated foreign interference
This allows commanders to spot weaknesses and refine strategy.
What Happens During the China Taiwan drills: China’s Military Tactics Explained
Although China does not release full details, previous exercises and available footage give a clear understanding of the tactics used.
1. Simulated Blockade Operations
Satellite imagery and statements indicate that China sets up military pressure around Taiwan in several stages:
Stage 1: Air and Sea Encirclement
Chinese aircraft and ships move into strategic zones around the island.
Stage 2: Long-Range Missile Simulations
Rocket force units prepare mock strikes on ports, airports, and radar stations.
Stage 3: Electronic Warfare
Systems jam Taiwan’s communications and GPS signals.
Stage 4: Amphibious Landing Practice
Troops rehearse small-scale landings on nearby coastal zones.
2. Cyber Operations and Information Warfare
China often runs coordinated online campaigns during drills. These may include:
- Propaganda messages
- Disinformation targeting Taiwanese morale
- Messaging aimed at deterring foreign intervention
3. Real-Time Surveillance and Target Mapping
Drones, satellites, and reconnaissance aircraft gather:
- Data on Taiwan’s radar responses
- The speed of Taiwan’s mobilization
- Weaknesses in defensive networks
This information helps China plan future operations.
China’s Messaging: The Political Narrative Behind the China Taiwan drills
Every major military operation from Beijing is accompanied by a carefully designed narrative for both domestic and global audiences.
1. Messaging to Taiwan
China frames the drills as a warning, claiming:
- Taiwan’s government is pursuing “independence.”
- China must act to protect national unity.
- Military force is justified if Taiwan crosses “red lines.”
2. Messaging to the United States
China wants to deter Washington by showing it is prepared for major conflict if necessary.
The underlying message is:
“US intervention will not stop us.”
3. Messaging to Regional Powers
Countries like Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Southeast Asian nations are also watching. China wants them to understand the cost of aligning too closely with Taiwan.
4. Messaging to the Chinese Population
State media emphasizes patriotism, unity, and strength.
It portrays the exercises as defensive and necessary.
Taiwan’s Immediate Military Response: High Alert and Close Monitoring
As news of the China Taiwan drills spread across the region, Taiwan’s Ministry of National Defense moved quickly to reassure citizens and global partners that the island remained secure and alert. Taiwan reported detecting multiple Chinese military aircraft, naval vessels, and missile platforms moving around the island in the early hours of the announcement.
Deployment of Air and Naval Forces
Taiwan quickly mobilized:
- Combat aircraft to track Chinese fighter jets
- Naval patrol ships to monitor PLAN (Chinese navy) movements
- Land-based missile systems to respond to potential threats
- Radar and surveillance units to evaluate China’s missile exercises
Taiwan’s air force scrambled several F-16Vs, Indigenous Defense Fighters (IDFs), and early-warning aircraft to ensure round-the-clock monitoring. The Ministry emphasized that Taiwan’s forces were “fully prepared” and had activated standard defense procedures.
Raising the Readiness Level
The Ministry of National Defense stated that Taiwan was on “high alert,” signaling a heightened state of readiness but avoiding actions that could escalate the situation unnecessarily. Officials stressed that Taiwan’s goal is defensive — not to provoke China but to maintain territorial integrity.
Public Messaging and Civil Confidence
Taiwan’s presidential office issued a stern response, calling the drills a threat to international order and an attempt to destabilize peace in the Taiwan Strait. At the same time, the government reassured citizens that the island’s military and defense systems remain robust.
Taiwan’s leadership understands that messaging is crucial. In times of military intimidation, maintaining public confidence is as important as military readiness.
President Lai Ching-te’s Strategy: “Strength, Stability, and Status Quo”
President Lai Ching-te, whom Beijing labels a “separatist,” has repeatedly emphasized that Taiwan will not seek conflict but will also not bow to intimidation. His stance is centered around three priorities:
1. Maintaining the Status Quo
Lai has openly stated that:
- Taiwan is already a sovereign nation, and therefore does not need to formally declare independence.
- The government will not initiate any provocative actions.
- Peace depends on both sides acting responsibly.
This strategy aligns with the majority of Taiwanese citizens who prefer neither unification nor formal independence.
2. Building Real Defensive Strength
Whether through missile technology, naval development, cyber defense, or air force upgrades, Lai insists that Taiwan’s survival depends on strong deterrence capabilities. He has called Taiwan’s defense investment “a necessity, not a choice.”
3. Strengthening Global Partnerships
Taiwan is working closely with the US, Japan, and European partners to build diplomatic resilience and global support.
Lai’s message during the drills was clear:
“We want peace, but peace requires strength.”
Taiwan’s Long-Term Defense Strategy: Preparing for Future Challenges
The China Taiwan drills highlight how Taiwan is evolving its military approach. The island’s new defense strategy focuses on three core components.
1. Asymmetric Warfare: Small, Smart, and Fast
Taiwan cannot match China in terms of sheer military size. Instead, it is focusing on:
- Mobile missile units
- Stealth coastal defense weapons
- Small, agile naval vessels
- Anti-ship and anti-air defense
- Cyber resilience
- Drone technologies
The objective is simple: raise the cost of invasion beyond what China is willing to pay.
2. Civil Defense and Preparedness
In recent years, Taiwan has expanded civil defense training, including:
- Emergency drills
- Shelter readiness programs
- Community defense volunteers
- Digital threat awareness
These programs help ensure that Taiwan remains resilient even in worst-case scenarios.
3. Indigenous Military Production
Taiwan is strengthening its defense industry by building:
- Missile systems
- New-generation submarines
- Advanced fighter jets (planned)
- Surveillance platforms
This reduces reliance on foreign suppliers and ensures long-term security.
International Reaction to “Justice Mission 2025”
China’s exercises have drawn strong reactions from governments and defense analysts across the world. The Taiwan Strait is one of the most important trade routes globally, and any escalation would disrupt global supply chains — especially in technology and semiconductor manufacturing.
United States: Support for Taiwan and Condemnation of China’s Actions
The United States remains Taiwan’s strongest security partner. Washington criticized the China Taiwan drills as destabilizing and unnecessary. Several US officials described the exercises as “coercive” and “dangerous.”
1. US Naval Presence in the Region
The US maintains a strong presence through:
- The US Seventh Fleet, stationed in Japan
- Regular patrols through the Taiwan Strait
- Joint exercises with Japan, South Korea, and Australia
This presence is meant to deter conflict and ensure freedom of navigation.
2. The $11 Billion Arms Package
Washington’s latest arms sale to Taiwan includes systems that significantly enhance Taiwan’s defensive capabilities. This includes:
- Air defense missile upgrades
- Anti-ship missile platforms
- Surveillance radars
- Technical support
The US insists these systems are meant to preserve peace, not provoke China.
3. Diplomatic Messaging from Washington
The US State Department emphasized that China’s actions “risk escalating regional tensions” and urged all parties to act responsibly. Washington reaffirmed its commitment to the Taiwan Relations Act, which requires the US to support Taiwan’s self-defense capability.
Japan’s Reaction: Rising Worries and Diplomatic Strain
Japan reacted strongly to the China Taiwan drills, as the island lies extremely close to Japanese territory. Several Japanese islands, including Yonaguni, are just over 100 km from Taiwan.
1. Japan’s Security Concerns
Japan fears that a conflict in Taiwan would:
- Endanger Japanese shipping routes
- Threaten nearby islands
- Pull Japan into a potential battle under its security alliance with the US
Japan’s military leadership has repeatedly stated that Taiwan’s security is directly connected to Japan’s security.
2. Sanae Takaichi’s Statement and Its Fallout
Japan’s leader Sanae Takaichi recently suggested that Japan’s Self-Defense Forces could intervene if Taiwan were attacked.
China reacted furiously, issuing warnings and travel advisories. Beijing accused Japan of “interfering in China’s internal affairs.”
3. Radar Lock Incident
Japan lodged a strong protest after Chinese fighter jets locked their radars on Japanese aircraft during training. Radar lock is considered a hostile act because it indicates targeting for missile launch.
This incident raised alarm across the region and further strained China-Japan relations.
European Union’s Perspective: Stability and Rule of Law
European nations have become increasingly vocal about tensions in the Taiwan Strait. Although Europe is not militarily involved, it has huge economic stakes in Asia.
EU officials expressed concern that:
- China’s drills undermine global stability
- Peaceful dialogue is essential
- Escalation would harm global trade and semiconductor supply chains
Several European parliaments have sent delegations to Taiwan in recent years, signaling growing support despite Beijing’s objections.
Australia and Southeast Asia: Cautious but Concerned
Countries in Southeast Asia are watching closely. Many have strong economic ties to China but also rely heavily on stability in the South China Sea and Taiwan Strait.
Regional concerns include:
- Impact on shipping lanes
- Increased militarization
- Potential spillover into the South China Sea disputes
Australia, under its AUKUS partnership with the US and UK, has openly criticized China’s drills as “provocative.”
How the Drills Affect Global Supply Chains
The Taiwan Strait handles one of the world’s busiest shipping routes.
Any conflict or blockade would disrupt:
- Semiconductor exports
- Oil and energy shipments
- Global electronics manufacturing
- Automotive supply chains
- International trade routes
Because Taiwan produces more than 60% of the world’s advanced chips, disruptions here would impact almost every global industry. Analysts warn that even temporary blockades could trigger shortages and economic instability.
Economic Impact on China Taiwan drills
Both economies are deeply interconnected with global markets, so military escalation carries major risks.
Impact on Taiwan
- Investor uncertainty
- Pressure on currency and markets
- Increased defense spending
- Potential impact on trade
However, Taiwan’s economy has historically shown resilience during past crises.
Impact on China
China risks:
- Reduced foreign investment
- Rising tensions with the US and Japan
- Threats to its export-driven economy
- Higher military costs
China must balance domestic nationalism with economic realities.
Why Regional Tensions Are Increasing in 2025
The China Taiwan drills are part of a broader pattern of rising Indo-Pacific tensions driven by:
- Strategic competition between the US and China
- Taiwan’s democratic resilience
- Japan’s security reforms
- Territorial disputes in the South China Sea
- China’s internal politics and national pride
As major powers jockey for influence, Taiwan sits at the center of a complex geopolitical contest.
Expert Analysis: What the 2025 Drills Reveal About China’s Military Strategy
Military analysts around the world have been closely studying the China Taiwan drills to understand Beijing’s evolving strategy. Unlike past exercises, “Justice Mission 2025” shows new levels of joint-force coordination, precision, and political signalling. Several defense experts believe the drills offer a preview of China’s future military operations.
1. China Is Practicing a Full Encirclement Strategy
Experts note that the exercises are not limited to symbolic shows of force. They involve:
- Multi-directional air incursions
- Naval blockades of key maritime routes
- Simulated missile strikes on Taiwan’s infrastructure
- Surveillance operations targeting command centers
This suggests China wants to demonstrate that it can control Taiwan’s surrounding waters and airspace, even if it does not initiate a full invasion. A blockade is considered by many analysts as a more realistic first step, as it would disrupt Taiwan’s economy while avoiding immediate ground combat.
2. Increased Use of Cyber Warfare and Electronic Attacks
Cybersecurity experts observed increased online activity from Chinese-linked hacking groups during the drills. These attempts included:
- Disrupting Taiwanese communication networks
- Targeting government websites
- Collecting intelligence on military responses
Electronic warfare units also tested signal jamming and radar interference. This indicates that China plans to use non-kinetic tools to weaken Taiwan before any possible physical conflict.
3. Testing Real-Time Coordination Between Military Branches
China’s army, navy, air force, and rocket force rarely conduct synchronized drills at this scale. Analysts believe the drills show China is transitioning to a modern, integrated warfighting doctrine. This shift mirrors US and NATO tactics, where all branches operate as a unified force.
4. Messaging to the Region: China Controls the Tempo
By launching the drills shortly after the US arms sale, China wants to send a message that it controls the pace of tensions. Beijing wants Japan, South Korea, and Southeast Asia to understand that it can escalate or de-escalate military pressure whenever it chooses.
5. Domestic Nationalism Is Influencing Military Decisions
Experts also believe domestic politics plays a major role. As China faces economic challenges at home, nationalist narratives help divert attention and reinforce the government’s authority. Military strength has become a symbolic representation of China’s rise.
Future Risks: What Could Happen in the Coming Months China Taiwan drills?
The China Taiwan drills raise several concerns among global security experts. While a full-scale war is not imminent, tensions are increasing in ways that could lead to miscalculations.
1. Risk of Accidental Conflict
With Chinese and Taiwanese aircraft flying close to each other, and US warships patrolling nearby waterways, the risk of accidental collisions is rising. A single mistake or misinterpreted action could ignite a larger conflict.
2. Increasing Frequency of Drills
Analysts predict that China may begin holding military exercises around Taiwan more frequently, possibly turning them into a new normal. If drills continue at this pace, Taiwan’s defense resources could be stretched thin.
3. Stronger US and Japan Military Coordination
As China steps up pressure, the US and Japan may increase:
- Joint military exercises
- Intelligence sharing
- Naval patrols
- Defense cooperation with Taiwan
This could further irritate Beijing and intensify regional tension.
4. Intensified Cyber Operations
Cyber warfare will continue to be one of the biggest risks. Attacks on critical infrastructure — such as power grids, communications, or financial systems — could cause major disruptions.
5. China’s Domestic Climate
China’s internal political priorities, economic pressures, and leadership objectives may influence future decisions. If the government feels external conflict can unite the public, tensions may escalate further.
Three Possible Future Scenarios
Security analysts outline three major scenarios that could unfold following the China Taiwan drills.
Scenario 1: Continued Tensions Without Conflict (Most Likely)
In this scenario:
- China continues frequent drills
- Taiwan strengthens defenses
- The US increases support
- Japan and regional allies remain cautious
- No side takes extreme action
This scenario preserves the status quo but keeps the region on edge. It is the most likely outcome because a war would be extremely costly for all sides.
Scenario 2: Limited Blockade or Economic Pressure
China could attempt a partial or symbolic blockade, such as:
- Blocking supply routes
- Targeting specific trade zones
- Delaying shipping through customs
- Imposing new economic restrictions
This would allow China to pressure Taiwan without a full-scale war.
Scenario 3: Full Military Conflict (Least Likely but Most Dangerous)
Although unlikely, analysts cannot rule out the possibility of:
- Missile strikes on Taiwan’s military bases
- Naval clashes in the Taiwan Strait
- Air battles near Taiwanese airspace
- Attempts to seize offshore islands
This would trigger global economic disruption and likely draw in the United States and Japan.
How Media and Information Warfare Shape the Conflict
The modern Taiwan Strait conflict is not fought only with missiles and ships. It also unfolds across:
- Social media
- Television broadcasts
- Online propaganda
- Cyber campaigns
- Diplomatic messaging
China’s online strategy includes:
- Portraying Taiwan as unstable
- Depicting China as a “protector of peace”
- Attacking Taiwan’s leadership
- Influencing global opinion
During the current drills, Chinese state media released animated videos, slogans, and infographics depicting the exercise as a “punishment” for separatist actions.
Taiwan’s media strategy includes:
- Emphasizing calm and preparedness
- Highlighting China’s aggression
- Reinforcing public resilience
- Strengthening ties with foreign media
Maintaining public morale is one of Taiwan’s top priorities.
Impact on Global Diplomacy and Alliances: China Taiwan drills
The China Taiwan drills are reshaping diplomatic relationships across Asia and the West.
1. Strengthening US Allies
Countries like Japan, Australia, and South Korea have deepened their security cooperation with the US, forming a stronger Indo-Pacific alignment.
2. Southeast Asian Balancing Act
Nations such as the Philippines, Vietnam, and Indonesia walk a fine line between China’s economic influence and regional security concerns. They want stability but do not wish to anger Beijing.
3. Europe’s Growing Interest
Europe has become more vocal in supporting Taiwan’s democracy and expressing concern over military intimidation. European delegations visiting Taiwan have increased in recent years.
Why Taiwan Matters to the World: China Taiwan drills
Taiwan plays a critical role in the global economy and international security.
1. Semiconductor Dominance
Taiwan produces:
- 63% of the world’s semiconductors
- Over 90% of the world’s advanced chips
Global industries—including smartphones, cars, computers, and AI—depend on Taiwan’s chip manufacturers.
2. Trade Routes
The Taiwan Strait is one of the world’s busiest maritime passages. A conflict here would affect:
- Oil shipments
- Container cargo
- Supply chains connecting Asia, Europe, and the US
3. Democratic Values
Taiwan is seen as a model of democracy in Asia. Many countries view its success as an example of democratic resilience.
Conclusion: What the China Taiwan drills Mean for 2025 and Beyond
The China Taiwan drills have sent shockwaves across the region and revealed how fragile peace in the Indo-Pacific has become. China wants to demonstrate strength, intimidate Taiwan, and deter US and Japanese involvement. Taiwan, on the other hand, remains calm yet determined, strengthening its defenses while maintaining diplomatic ties.
The broader world is watching closely. The outcome of this ongoing confrontation will shape:
- Future security policies
- Global trade stability
- International alliances
- The power balance in Asia
As tensions grow, all parties face enormous responsibility. Taiwan must continue strengthening its defenses. China must weigh the economic and diplomatic costs of its assertiveness. The United States and its allies must promote stability while supporting democratic values.
Although the future remains uncertain, one fact is clear:
The Taiwan Strait will remain one of the world’s most important geopolitical flashpoints for years to come.
